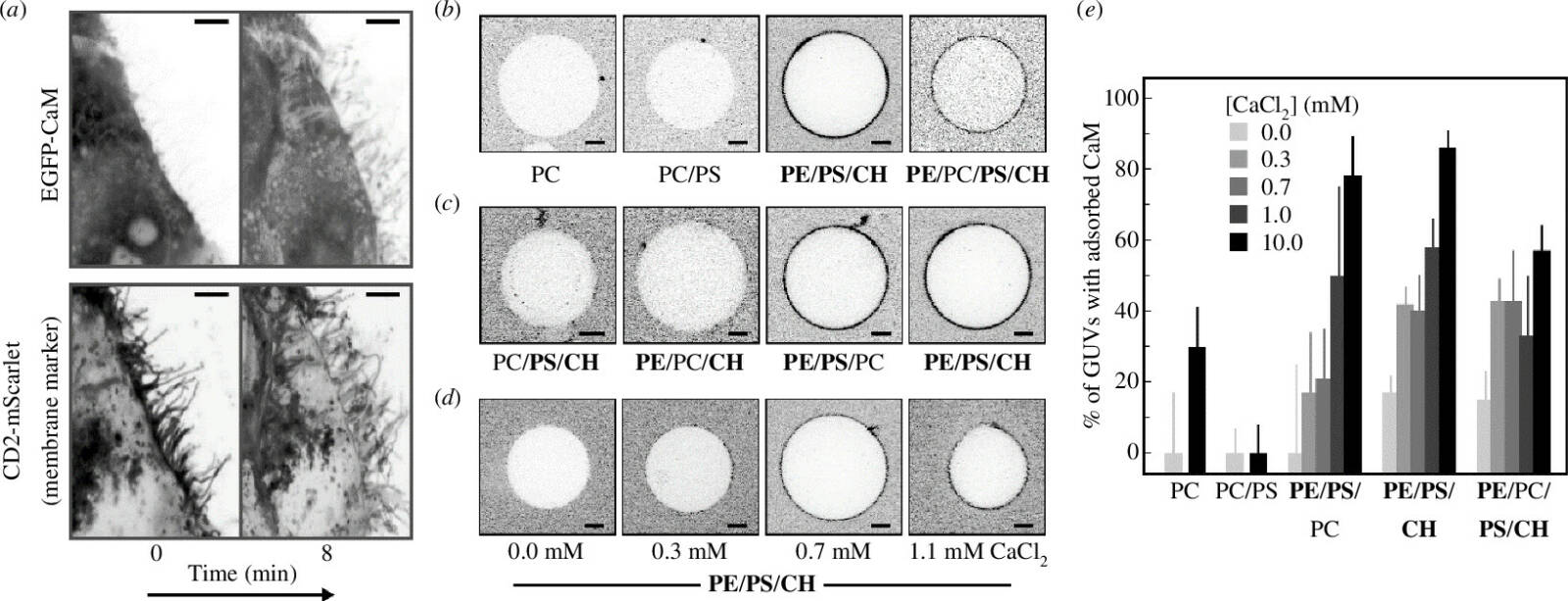
We used atomistic molecular dynamics simulations and various experimental approaches—including a plethora of fluorescence approaches—to study whether calmodulin could bind to the lipids in the cytosolic leaflet of the plasma membrane. We found that the negatively charged phosphatidylserine is crucial in attracting the calcium-loaded calmodulin to the membrane surface. Phosphatidylethanolamine is another key player: it both forms hydrogen bonds with calmodulin and destabilizes the membrane, leading to the exposure of lipid acyl chains that can interact with calmodulin.
The paper is openly available online!