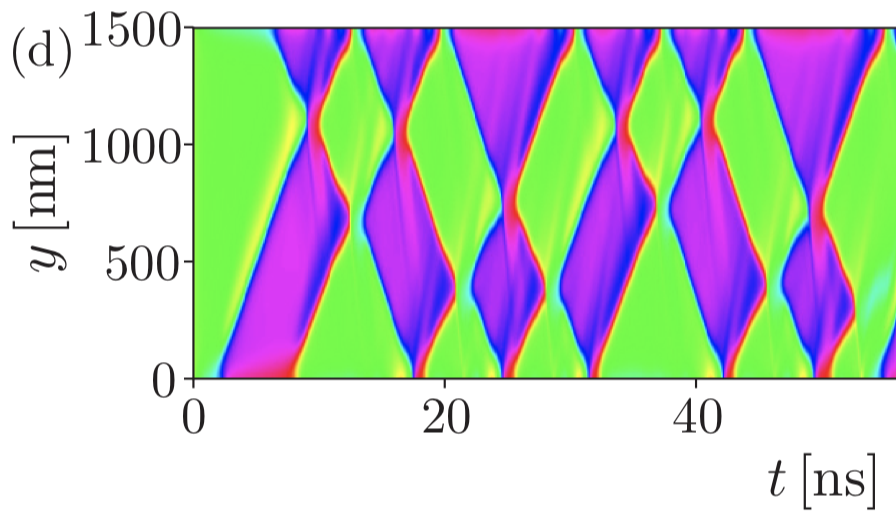
A well-known feature of magnetic field driven dynamics of domain walls in ferromagnets is the existence of a threshold driving force at which the internal magnetization of the domain wall starts to precess—a phenomenon known as the Walker breakdown—resulting in an abrupt drop of the domain-wall propagation velocity. Here, we report on micromagnetic simulations of magnetic field driven domain-wall dynamics in thin ferromagnetic strips with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy which demonstrate that in wide enough strips Walker breakdown is a multistep process: It consists of several distinct velocity drops separated by short linear parts of the velocity vs field curve. These features originate from the repeated nucleation, propagation, and annihilation of an increasing number of Bloch lines within the domain wall as the driving field magnitude is increased. This mechanism arises due to magnetostatic effects breaking the symmetry between the two ends of the domain wall.
Johanna Hütner, Touko Herranen, and Lasse Laurson, Multistep Bloch-line-mediated Walker breakdown in ferromagnetic strips, Phys. Rev. B. 99, 174427 (2019).