Software
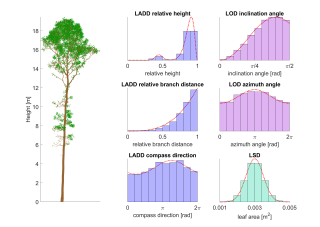 LeafGen: Foliage generation for QSMs and point clouds: the package (Matlab) containing methods for generating virtual foliage on 3D tree models based on parametric leaf distributions. The tree models can be either quantitative structure models (QSM) or point clouds of trees. The user can choose parametric distribution functions on variables of tree structure for the leaf area density distribution (LADD), leaf orientation distribution (LOD), and leaf size distribution (LSD).
LeafGen: Foliage generation for QSMs and point clouds: the package (Matlab) containing methods for generating virtual foliage on 3D tree models based on parametric leaf distributions. The tree models can be either quantitative structure models (QSM) or point clouds of trees. The user can choose parametric distribution functions on variables of tree structure for the leaf area density distribution (LADD), leaf orientation distribution (LOD), and leaf size distribution (LSD).
 Zeffiro Interface: the software package providing and accessible tool for finite element based forward and inverse simulations in EEG/MEG. It can also be used in other bioelectromagnetical imaging applications targeting the brain.
Zeffiro Interface: the software package providing and accessible tool for finite element based forward and inverse simulations in EEG/MEG. It can also be used in other bioelectromagnetical imaging applications targeting the brain.
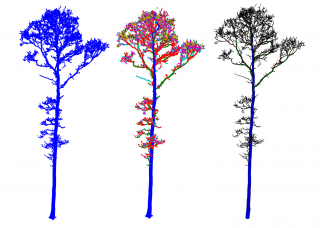 TreeQSM: the software package (Matlab) for reconstructing quantitative structure models of trees from laser scanner data.
TreeQSM: the software package (Matlab) for reconstructing quantitative structure models of trees from laser scanner data.

GPU-Torre and GPU-Torre-3D are open Matlab-based toolboxes for numerical investigation of mathematical non-linear tomographic radar inverse imaging problems in 2D and 3D.
Posters
Focal brain source imaging
Title
Adaptive Method for Bayesian EEG/MEG Source Localization to Support Treatment of Focal Epilepsy
Conference
Applied Inverse Problems 2023, AIP2023, Göttingen, Germany
Authors
Joonas Lahtinen, Alexandra Koulouri, Stefan Rampp, Jörg Wellmer, Carsten Wolters, Sampsa Pursiainen
Layout
Sampsa Pursiainen
Description
This study introduces a new method for the localization of the epileptogenic zone (EZ) in focal epilepsy, which builds upon the established success of standardized lowresolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA). By utilizing the resolution matrix of the lead field, sLORETA ensures a highly unbiased and accurate estimation of EZ even in the presence of measurement noise. The proposed methodology further improves the accuracy of sLORETA when combined with the Hierarchical Adaptive Lp Regression (HALpR) method, which relies on a conditionally exponential prior to simultaneously localize cortical and sub-cortical activity. The resulting method, referred to as Standardized Hierarchical Adaptive Lp Regression (SHALpR), has been shown to outperform its basic counterpart, Standardized Shrinking LORETA-FOCUSS (SSLOFO), and sLORETA in localizing brain activity. We demonstrate the potential of SHALpR in improving the diagnosis and treatment of focal epilepsy, as accurate localization of EZ is essential for successful surgical interventions. By providing a robust and accurate methodology for EZ localization, this study contributes to the ongoing efforts to advance the understanding and treatment of epilepsy.
Automatic tree species recognition
Title
Automatic tree species recognition with quantitative structure models
Conference
Royal Society Meeting: The terrestrial laser scanning revolution in forest ecology
Authors
M. Åkerblom, P. Raumonen, R. Mäkipää and M. Kaasalainen
Layout
M. Åkerblom
Description
We present a highly-accurate tree species recognition approach that uses only 3D spatial terrestrial laser scanning data (TLS) and is fully automatic. Individual trees are automatically separated from forest plot level point clouds and reconstructed as a cylindrical quantitative structure model (QSM). As a QSM contains the comprehensive geometric and topological structure of a tree, we have access to tree properties that are impossible to compute directly from point cloud data without reconstructing full QSMs. In comparison, previous methods require at least some level of manual interaction to separate individual trees, and they often rely on additional data sources, e.g., hyperspectral data.
We defined 15 classification features and tested their performance on over 1200 trees from 3 different species, and 5 different classification methods. We used trees from three single-species and two mixed-species forest plots, all located in Finland. The results show that accurate species classification based on TLS data and QSMs is possible when suitable training data are available. Our tests showed that as little as 30 training samples per species can produce good results. All of the classification methods performed well and maximum classification accuracy was over 95 % for all of the methods.
Reference
| Automatic tree species recognition with quantitative structure models In Remote Sensing of Environment, volume 191, 2017. |
Disseminating reconstructed tree models
Title
Disseminating reconstructed tree models
Conference
International Boreal Forest Research Association (IBFRA 2015)
Authors
M. Åkerblom, S. Kaasalainen, P. Raumonen and M. Kaasalainen
Layout
M. Åkerblom
Description
For about two years our research team at Tampere University of Technology has been disseminating research results in the form of animations, interactive 3D models and Facebook updates. The animations showcase how the methods we have developed can be used to reconstruct tree models from terrestrial laser scanning data. The computations are done in Matlab, and the results are exported to Blender – an open-source 3D modeling and animation software – to make data-driven animations that are later uploaded to the group’s Youtube channel and further shared on our research consortium’s Facebook page. Some of the resulting models have also been published as interactive 3D models that can be viewed in a standard web browser supporting WebGL technology. The extensive, positive feedback has shown that these innovative dissemination channels are vital for helping others understand the research methods and results without getting lost in the details.
FSPM 2013
Title
Fast automatic method for constructing topologically and geometrically precise tree models from TLS Data
Conference
7th International Conference on Functional-Structural Plant Models
Authors
P. Raumonen, E. Casella, M. Disney, M. Åkerblom and M. Kaasalainen
Layout
M. Åkerblom and P. Raumonen
Description
We present a computational method that produces automatically precision models of trees from terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) data. The method is fast, typically few minutes per tree, and the resulting model contains both the topological and geometrical information of the tree. The method is validated using artificial and real TLS data. The results show that TLS together with computational reconstruction method provides means to collect structural information of trees fast and nondestructively.
Reference
| Fast automatic method for constructing topologically and geometrically precise tree models from TLS Data, In 7th International Conference on Functional-Structural Plant Models (FSPM2013) Proceedings, 2013. [cite] [url] |
Presentations
Automatic species recognition with QSMs
A presentation on automatic tree species recognition presented by M. Åkerblom at UCL on March 1st, 2017. The content requires JavaScript and Flash Player to work. Created with Prezi.
The presentation goes over the poster on the same topic and the Automatic species recognition video was also shown during the presentation.
AudioSlides: Automatic tree species recognition with quantitative structure models
A slide presentation with an audio track for the paper Automatic tree species recognition with quantitative structure models. The presentation summarises the context and results of the species recognition study. You can also download a PDF version without any audio.
Quantitative structure tree models from terrestrial laser scanner data
Presentation on quantitative structure models given by P. Raumonen at the Silvilaser 2015 conference in September 2015.
Disseminating tree models and other research results
A presentation on our groups dissemination methods given by M. Åkerblom in the Innovative means to disseminate scientific information session of the IBFRA 2015 conference. The content requires JavaScript and Flash Player to work. Created with Prezi.
If you prefer a more traditional format, this presentation is also available as a PDF version, but do note that the Prezi version also contains videos.
Massive-scale tree modelling from TLS data
The presentation was made using HTML and JavaScript libraries impress.js and d3.js and should therefore work in any modern web browser. Arrow keys and spacebar can be used to switch slides.
Datasets
Asteroid wireframe package
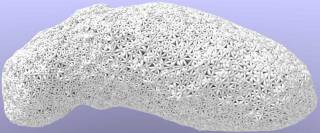
Asteroid Wireframe Package: a dataset and code package for creating complex-shaped, permittivity-controlled analogue objects for 3D-printing.
Sorsa, Liisa-Ida, et al. “Complex-structured 3D-printed wireframes as asteroid analogues for tomographic microwave radar measurements.” Materials & Design 198 (2021): 109364.
HSL incidence angle measurements and results
Authors
S. Kaasalainen, M. Åkerblom and M. Kaasalainen
Format
.MAT-file (MATLAB)
Release date
Measurement data for the article Uncertainty caused by incidence angle effects on vegetation spectral indices from multispectral lidar, including angle and incidence data and resulting model fitting parameters.










