Anssi Auvinen | Epidemiology
A randomized trial of early detection of clinically significant prostate cancer.
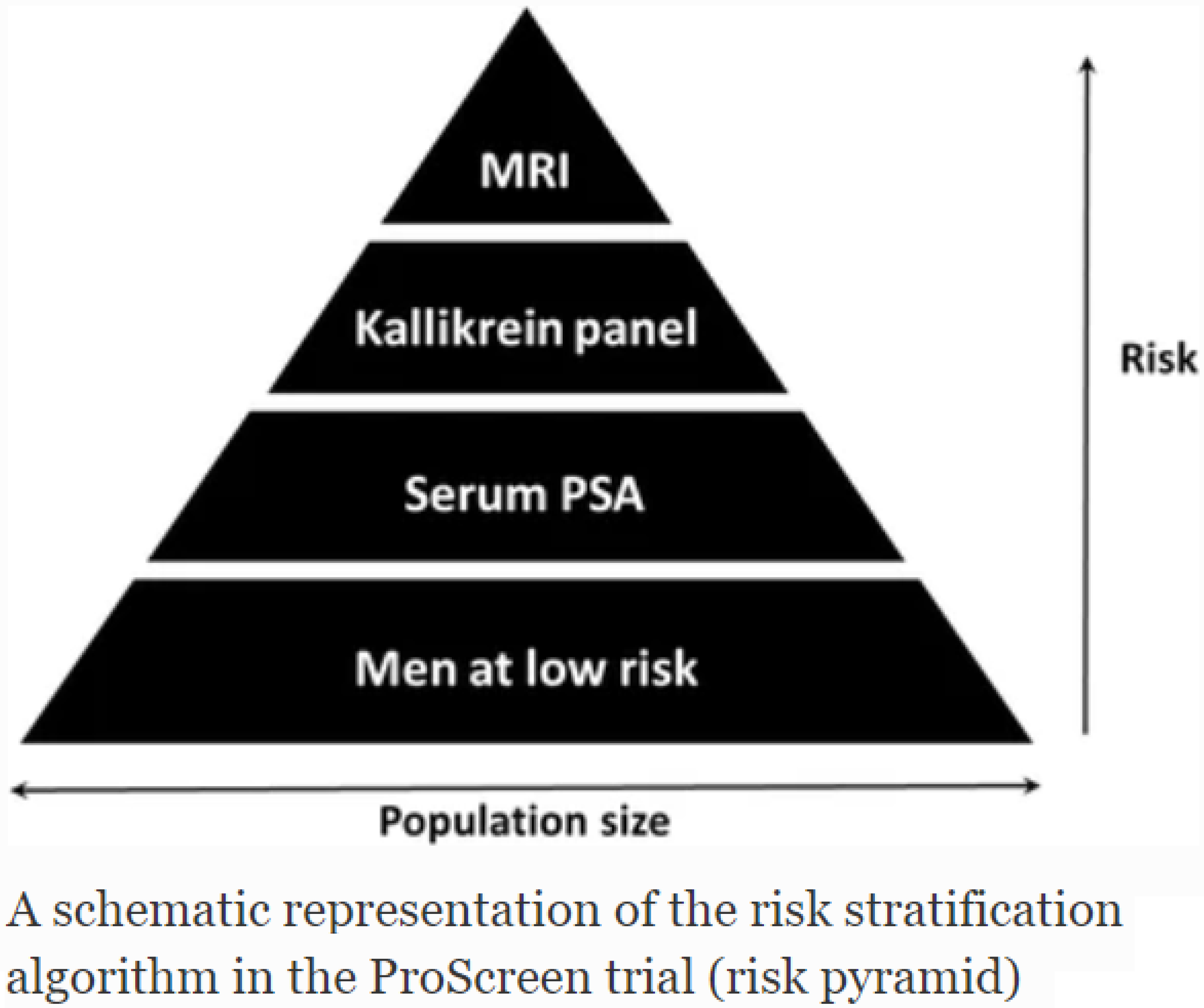
The ProScreen trial has a target sample size of 115,000 men. All men will be randomized during 2024, and the first screening round completed in 2025. Currently the second and third screening rounds are on-going.
The first results have published (Auvinen et al. JAMA 2024) and they indicate that the ProScreen screening algorithm has succeeded in reducing the detection of low-risk cases while detecting substantial numbers of high-risk cancers.
We will next analyze potential ways to improve the screening algorithm, and evaluate prognostic features in screen-detected cancers and assess the sensitivity of the screening algorithm.
Auvinen A, Tammela T, Mirtti T, Lilja H, Tolonen T, Kenttämies A, Rinta-Kiikka I, Lehtimäki T, Natunen K, Nevalainen J, Raitanen J, Ronkainen J, van der Kwast T, Riikonen J, Pétas A, Matikainen M, Taari K, Kilpeläinen T, Rannikko AS. Prostate cancer screening with PSA, kallikrein panel and MRI: The ProScreen randomized trial. JAMA 2024;331:1452-59
Rannikko A, Leht M, Mirtti T, Kenttämies A, Tolonen T, Rinta-Kiikka I, Kilpeläinen TP, Natunen K, Lilja H, Lehtimäki T, Raitanen J, Kujala P, Ronkainen J, Matikainen M, Petas A, Taari K, Tammela T, Auvinen A. Population-based randomized trial of screening for clinically significant prostate cancer: A pilot study. BJU Int 2022;130:193-199
Steven Bova | PELICAN-Personalized Cancer Medicine
Cancer origin tracing and timing in two high-risk prostate cancers using multisample whole genome analysis: prospects for personalized medicine
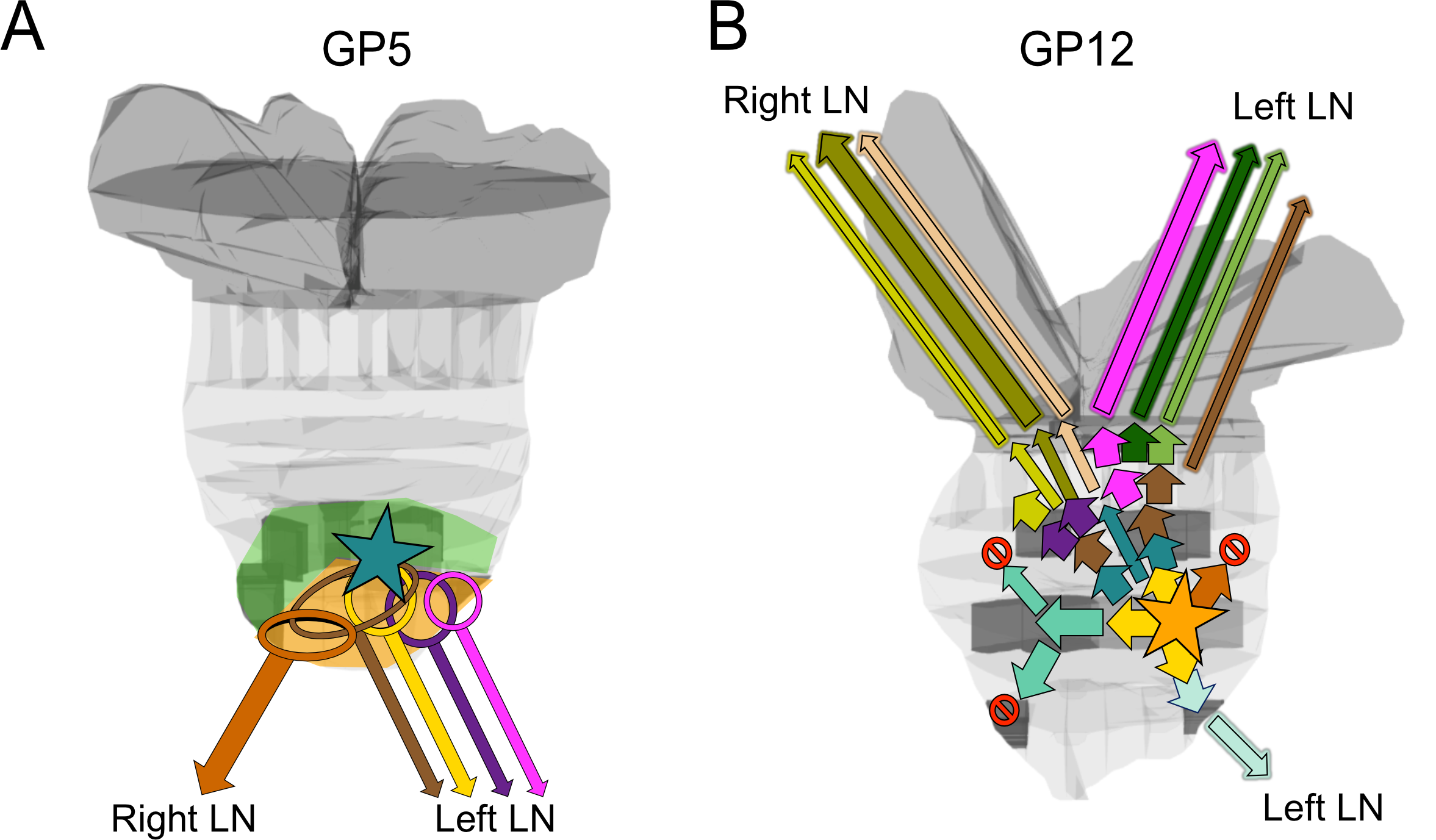 We used novel processing techniques to obtain whole genome data together with 3D anatomic and histomorphologic analysis in two men (GP5 and GP12) with high‐risk PrCa undergoing radical prostatectomy. We inferred the timing of origin and spread of each cancer, with potential clinical implications. Multiple metastasis‐originating events were identified in each patient and tracked anatomically. Metastasis from prostate to lymph nodes occurred strictly ipsilaterally in all 12 detected events. In this pilot, metastatic subclone content analysis appears to substantially enhance the identification of key drivers. Evolutionary analysis’ potential impact on therapy selection appears positive in these pilot cases.
We used novel processing techniques to obtain whole genome data together with 3D anatomic and histomorphologic analysis in two men (GP5 and GP12) with high‐risk PrCa undergoing radical prostatectomy. We inferred the timing of origin and spread of each cancer, with potential clinical implications. Multiple metastasis‐originating events were identified in each patient and tracked anatomically. Metastasis from prostate to lymph nodes occurred strictly ipsilaterally in all 12 detected events. In this pilot, metastatic subclone content analysis appears to substantially enhance the identification of key drivers. Evolutionary analysis’ potential impact on therapy selection appears positive in these pilot cases.
Kirsi Rautajoki (priorly Granberg) | Cancer Regulation and Immunology
Tumor immune microenvironment analysis reveals three tumor subgroups
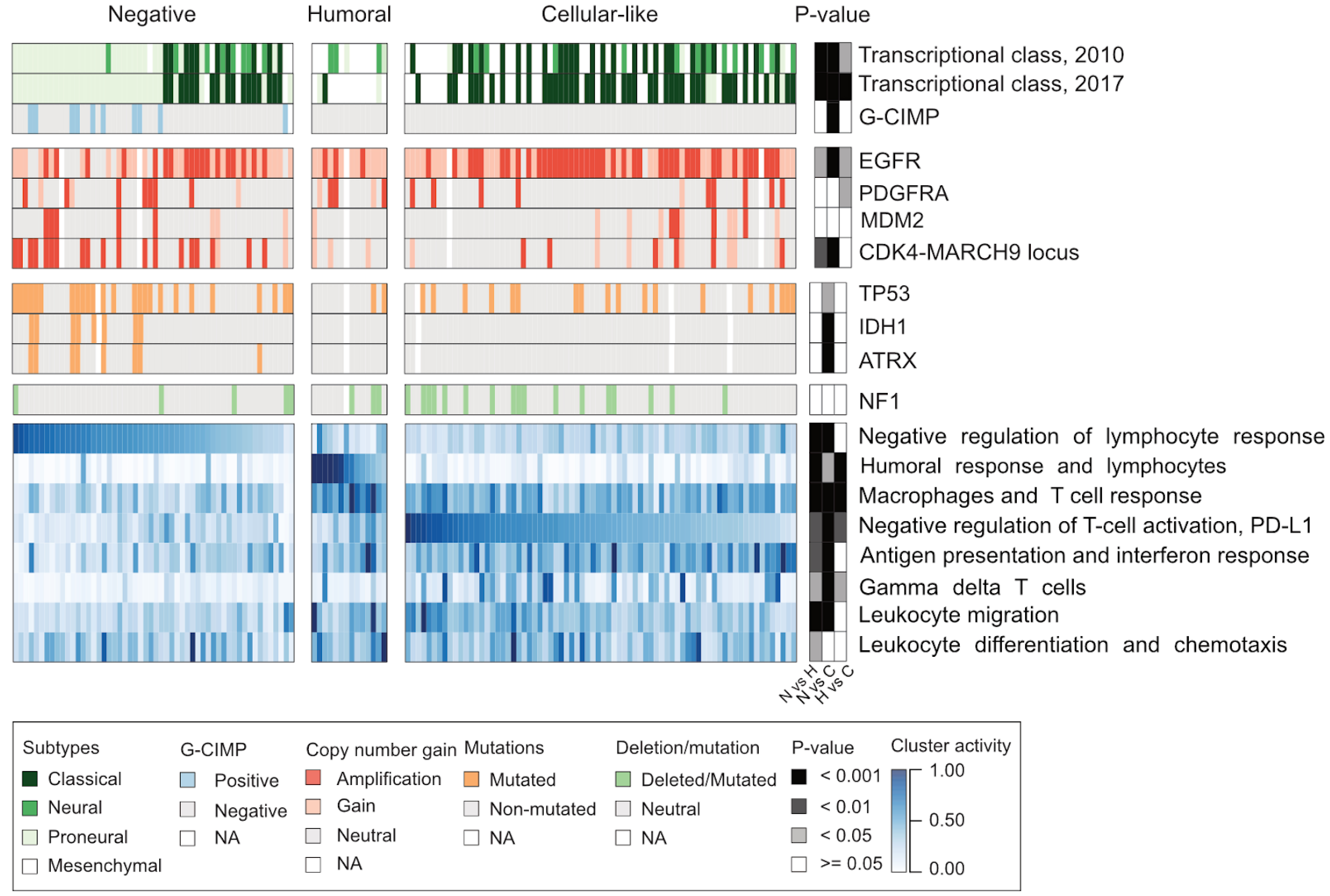 Understanding the nature of immunosuppression in malignant tissue is important for successful cancer treatment through immune system modulation. In this study, we uncovered high variability in immune system-related responses and in the composition of the microenvironment across glioblastoma (GBM) cohort, suggesting immunologic diversity. Our analysis identified three GBM subgroups presenting different adaptive immune responses: negative, humoral, and cellular-like. These subgroups and immune cell compositions were associated with typical alterations, such as CDK4 amplifications or inactivating NF1 alterations. All IDH-mutated samples were in the negative group, and they showed lower expression and higher DNA methylation of MHC-I genes.
Understanding the nature of immunosuppression in malignant tissue is important for successful cancer treatment through immune system modulation. In this study, we uncovered high variability in immune system-related responses and in the composition of the microenvironment across glioblastoma (GBM) cohort, suggesting immunologic diversity. Our analysis identified three GBM subgroups presenting different adaptive immune responses: negative, humoral, and cellular-like. These subgroups and immune cell compositions were associated with typical alterations, such as CDK4 amplifications or inactivating NF1 alterations. All IDH-mutated samples were in the negative group, and they showed lower expression and higher DNA methylation of MHC-I genes.
Luoto S, Hermelo I, Vuorinen E, Hannus P, Kesseli J, Nykter M, Granberg KJ
Cancer Res. 2018 78(19):5574-5585.
Luoto et al. – 2018 – Computational Characterization of Suppressive Immu
Teemu Murtola | Pharmacoepidemiology and Chemoprevention
Atorvastatin Versus Placebo for Prostate Cancer Before Radical Prostatectomy-A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial
 We tested whether intervention with atorvastatin affects the prostate beneficially compared with placebo in men with prostate cancer in a randomized clinical trial. A total of 160 statin-naïve prostate cancer patients scheduled for radical prostatectomy were randomized to use 80 mg atorvastatin or placebo daily from recruitment to surgery for a median of 27 d. Cholesterol-lowering atorvastatin does not lower prostate cancer proliferation rate compared with placebo overall, but exploratory analyses suggest a benefit in longer exposure.
We tested whether intervention with atorvastatin affects the prostate beneficially compared with placebo in men with prostate cancer in a randomized clinical trial. A total of 160 statin-naïve prostate cancer patients scheduled for radical prostatectomy were randomized to use 80 mg atorvastatin or placebo daily from recruitment to surgery for a median of 27 d. Cholesterol-lowering atorvastatin does not lower prostate cancer proliferation rate compared with placebo overall, but exploratory analyses suggest a benefit in longer exposure.
Murtola TJ, Syvälä H, Tolonen T, Helminen M, Riikonen J, Koskimäki J, Pakarainen T, Kaipia A, Isotalo T, Kujala P, Tammela TLJ.
Eur Urol. 274:697-701, 2018.
Matti Nykter | Computational Biology
Integrative proteogenomics in prostate cancer
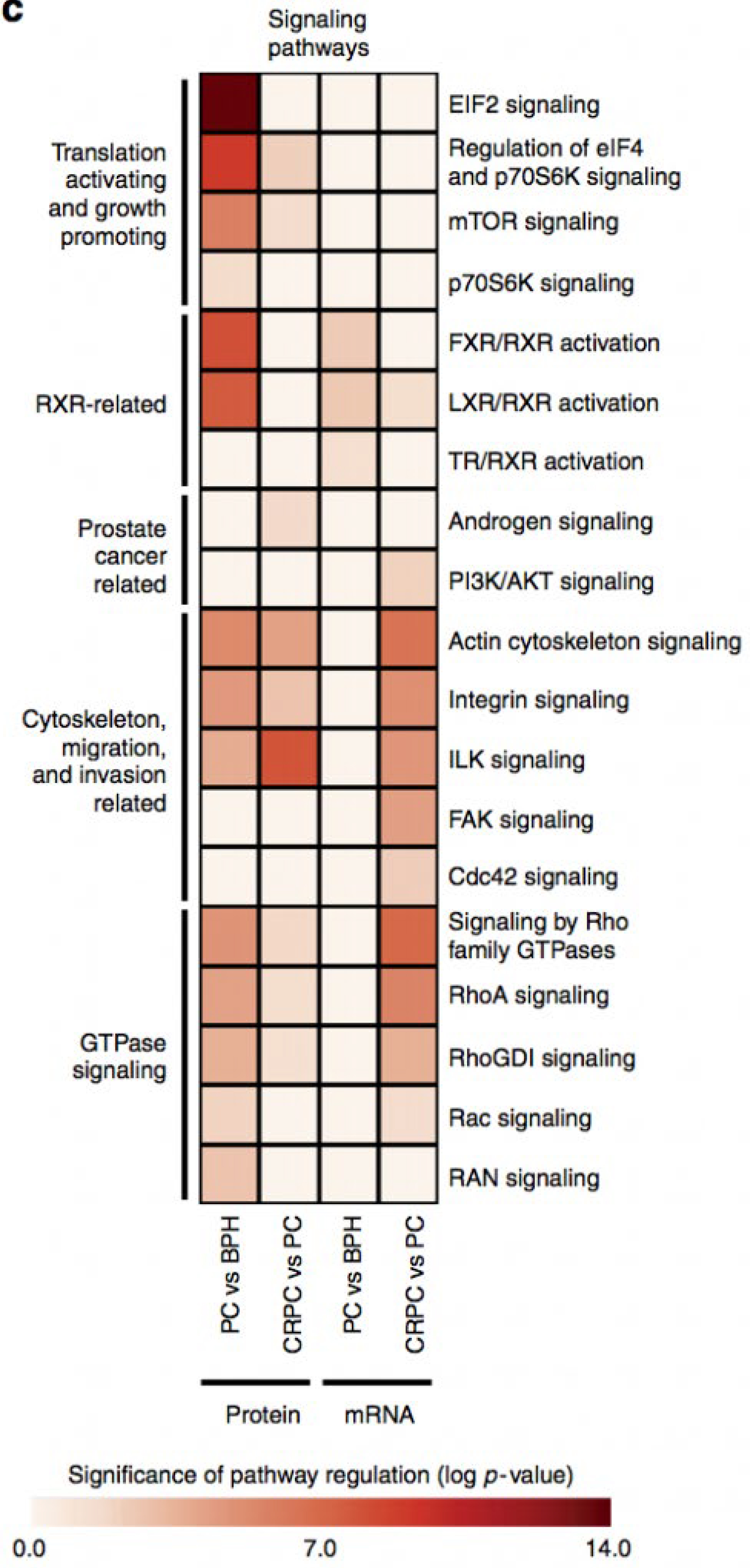 We report high-throughput mass spectrometry with integrated genome level analysis on clinical tissue samples of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), untreated primary prostate cancer (PC) and castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Each sample group shows a distinct protein profile. We show that, especially in CRPC, gene copy number, DNA methylation, and RNA expression levels do not reliably predict proteomic changes. Instead, we uncover previously unrecognized molecular and pathway events, for example, several miRNA target correlations present at protein but not at mRNA level. Notably, we identify two metabolic shifts in the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) during prostate cancer development and progression.
We report high-throughput mass spectrometry with integrated genome level analysis on clinical tissue samples of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), untreated primary prostate cancer (PC) and castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Each sample group shows a distinct protein profile. We show that, especially in CRPC, gene copy number, DNA methylation, and RNA expression levels do not reliably predict proteomic changes. Instead, we uncover previously unrecognized molecular and pathway events, for example, several miRNA target correlations present at protein but not at mRNA level. Notably, we identify two metabolic shifts in the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) during prostate cancer development and progression.
See Research highlight article “Controlling Mutational Chaos” in Nature Reviews Urology.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41585-018-0021-1
Latonen et al. – 2018 – Integrative proteomics in prostate cancer uncovers
Pekka Ruusuvuori | Bioimage Informatics
Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and grading of prostate cancer in biopsies
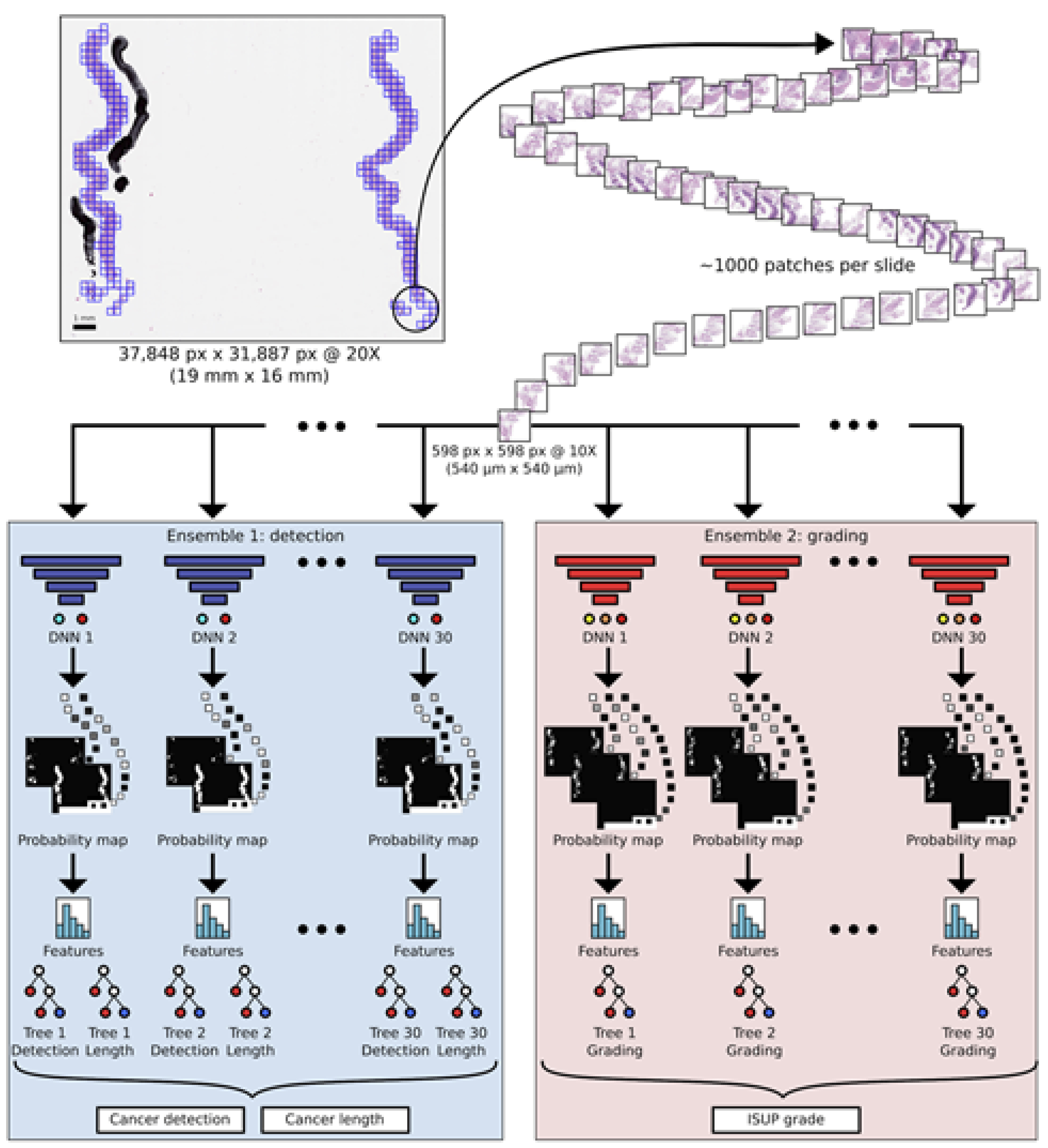 We report pathologist level accuracy for artificial intelligence based detection, length estimation and grading of prostate cancer from histopathological images in a population based diagnostic study in a collaboration study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet.
We report pathologist level accuracy for artificial intelligence based detection, length estimation and grading of prostate cancer from histopathological images in a population based diagnostic study in a collaboration study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(19)30738-7/fulltext
Ström, P., Kartasalo, K., Olsson, H., Solorzano, L., Delahunt, B., Berney, D. M., Iczkowski, K. A., Kench, J.G., Kristiansen, G., van der Kwast, T.H., Leite, K.R.M., McKenney, J.K., Oxley, J., Pan, C., Samaratunga, H., Srigley, J.R., Takahashi, H., Tsuzuki, T., Varma, M., Zhou, M., Lindberg, J., Lindskog, C., Ruusuvuori, P., Wählby, C., Grönberg, H., Rantalainen, M., Egevad, L., Eklund M. (2020).
Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and grading of prostate cancer in biopsies: a population-based, diagnostic study.
The Lancet Oncology, 21(2), 222-232.
Ström et al. – 2020 – Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and grading_
Johanna Schleutker | Genetic Predisposition to Prostate Cancer
Implications of the 19q13 Aggressive Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Locus
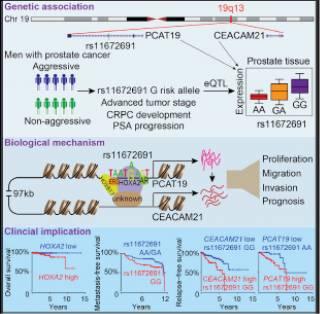 We found an association of the aggressive PCa-associated allele G of rs11672691 with elevated transcript levels of two biologically plausible candidate genes, PCAT19 and CEACAM21, implicated in PCa cell growth and tumor progression. Mechanistically, rs11672691 resides in an enhancer element and alters the binding site of HOXA2, a novel oncogenic transcription factor with prognostic potential in PCa. Remarkably, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated single-nucleotide editing showed the direct effect of rs11672691 on PCAT19 and CEACAM21 expression and PCa cellular aggressive phenotype. Clinical data demonstrated synergistic effects of rs11672691 genotype and PCAT19/CEACAM21 gene expression on PCa prognosis.
We found an association of the aggressive PCa-associated allele G of rs11672691 with elevated transcript levels of two biologically plausible candidate genes, PCAT19 and CEACAM21, implicated in PCa cell growth and tumor progression. Mechanistically, rs11672691 resides in an enhancer element and alters the binding site of HOXA2, a novel oncogenic transcription factor with prognostic potential in PCa. Remarkably, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated single-nucleotide editing showed the direct effect of rs11672691 on PCAT19 and CEACAM21 expression and PCa cellular aggressive phenotype. Clinical data demonstrated synergistic effects of rs11672691 genotype and PCAT19/CEACAM21 gene expression on PCa prognosis.
Gao P, Xia JH, Sipeky C, Dong XM, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Zhang P, Cruz SP, Zhang K, Zhu J, Lee HM, Suleman S, Giannareas N, Liu S; PRACTICAL Consortium, Tammela TLJ, Auvinen A, Wang X, Huang Q, Wang L, Manninen A, Vaarala MH, Wang L, Schleutker J, Wei GH.
Cell 174(3):576-589, 2018
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.003
Alfonso Urbanucci | Genomic Regulation for Precision Cancer Medicine
The optimal treatment for intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer (PC) patients is still unknown. Many patients with slow growing tumors would not require treatment but are overtreated because PSA screening is highly sensitive. The challenge in distinguishing these tumors lies in the unresolved complexity of the PC multifocality, metastatic potential, and tumor microenvironment.
Most studies assessing the extent of PC molecular heterogeneity and metastatic potential have characterised primary tumors focusing on DNA sequencing and genomic alterations using bulk methods. Biomarkers derived from these studies have not demonstrated clinically meaningful and superior predictive abilities compared to established clinico-pathological stratification systems. The research group uses single cell technology and examines cell composition from bulk tissue gene expression data to retrieve prognostic gene signatures associated with aggressive tumor behaviour.
Highlighted recent work from the group can be found from research groups home page
Tapio Visakorpi | Molecular Biology of Prostate Cancer
Androgen receptor and ERG drive the expression of prostate cancer specific long noncoding RNAs
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play pivotal roles in cancer development and progression, and some function in a highly cancer-specific manner. Here, we investigated a group of lncRNAs that we previously identified to be aberrantly expressed in prostate cancer, called TPCATs. We report that the majority of TPCATs investigated here are strongly associated with androgen receptor and other cooperative TFs, most importantly with ERG, in fusion-positive tumors. We found that the expression of many of the TPCATs was regulated by these TFs. In addition, three of the TPCATs were independently associated with PC progression, most notably EPCART that we also found to promote the migration and proliferation of the PC cells in vitro. Together, these findings demonstrate that EPCART has functions relevant for PC progression.
Kohvakka, A., Sattari, M., Shcherban, A., Annala, M., Urbanucci, A., Kesseli, J., Tammela, T., Kivinummi, K., Latonen, L., Nykter, M., Visakorpi, T. AR and ERG drive the expression of prostate cancer specific long noncoding RNAs.
Oncogene 39, 5241–5251 (2020).
Nonmetastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer and Survival with Darolutamide.
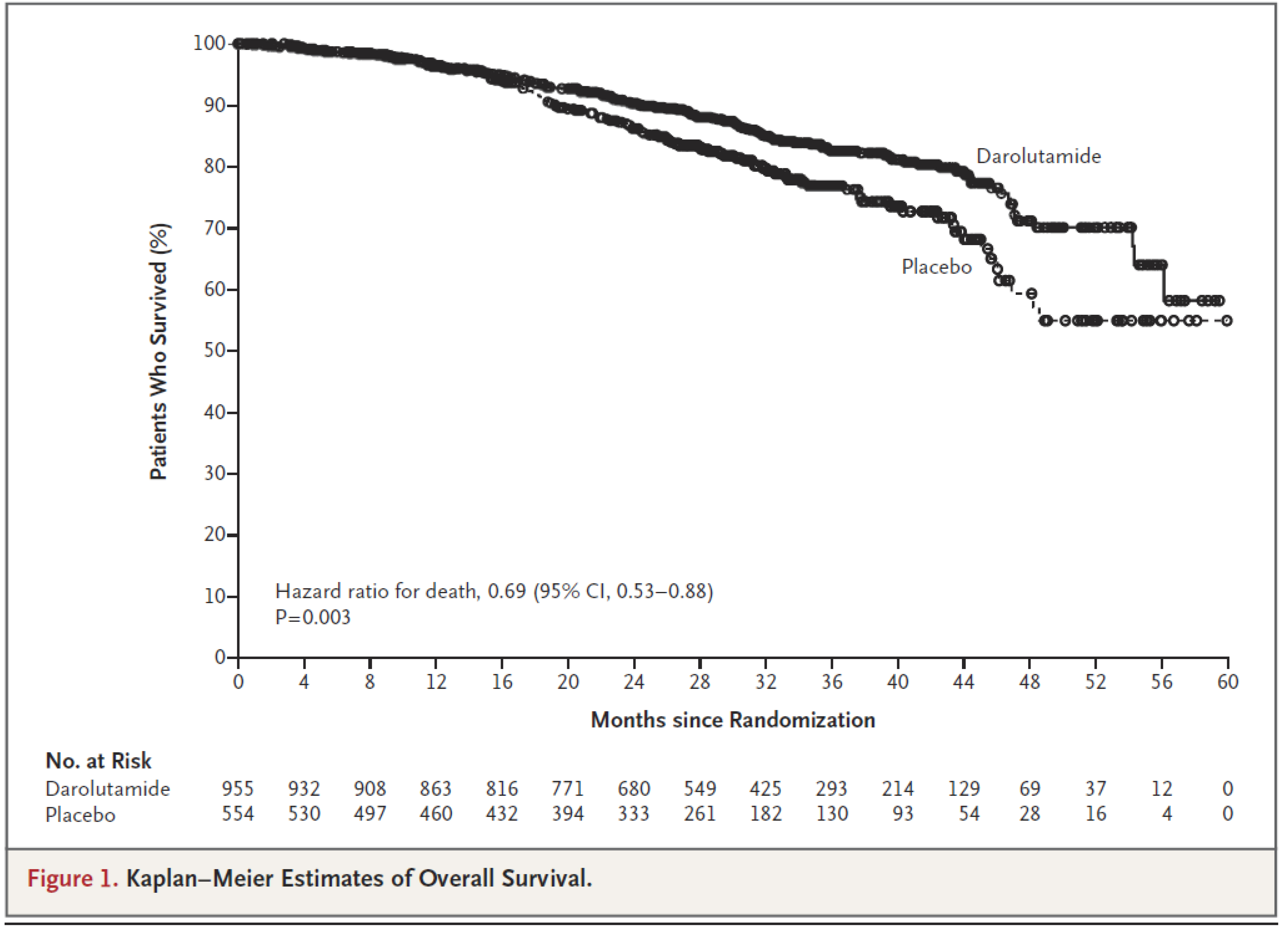 In this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, we randomly assigned 1509 men, in a 2:1 ratio, to receive darolutamide (955 patients) or placebo (554 patients) while they continued to receive androgen-deprivation therapy. After the results of the primary end-point analysis were found to be positive, unblinding of the treatment assignments occurred, and patients in the placebo group were permitted to cross over to receive open-label darolutamide treatment.Among men with nonmetastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer, the percentage of patients who were alive at 3 years was significantly higher among those who received darolutamide than among those who received placebo. The incidence of adverse events was similar in the two groups. (Funded by Bayer HealthCare and Orion Pharma; ARAMIS ClinicalTrials.gov number.
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, we randomly assigned 1509 men, in a 2:1 ratio, to receive darolutamide (955 patients) or placebo (554 patients) while they continued to receive androgen-deprivation therapy. After the results of the primary end-point analysis were found to be positive, unblinding of the treatment assignments occurred, and patients in the placebo group were permitted to cross over to receive open-label darolutamide treatment.Among men with nonmetastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer, the percentage of patients who were alive at 3 years was significantly higher among those who received darolutamide than among those who received placebo. The incidence of adverse events was similar in the two groups. (Funded by Bayer HealthCare and Orion Pharma; ARAMIS ClinicalTrials.gov number.
Fizazi K, Shore N, Tammela TL, Ulys A, Vjaters E, Polyakov S, Jievaltas M, Luz M, Alekseev B, Kuss I, Le Berre MA, Petrenciuc O, Snapir A, Sarapohja T, Smith MR; ARAMIS Investigators.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Sep 10;383(11):1040-1049.
Fizazi et al. – 2020 – Nonmetastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cance
Teemu Tolonen | Histopathology
Extraprostatic extension (pT3a) in prostate biopsy is an under-recognized feature indicating high risk disease
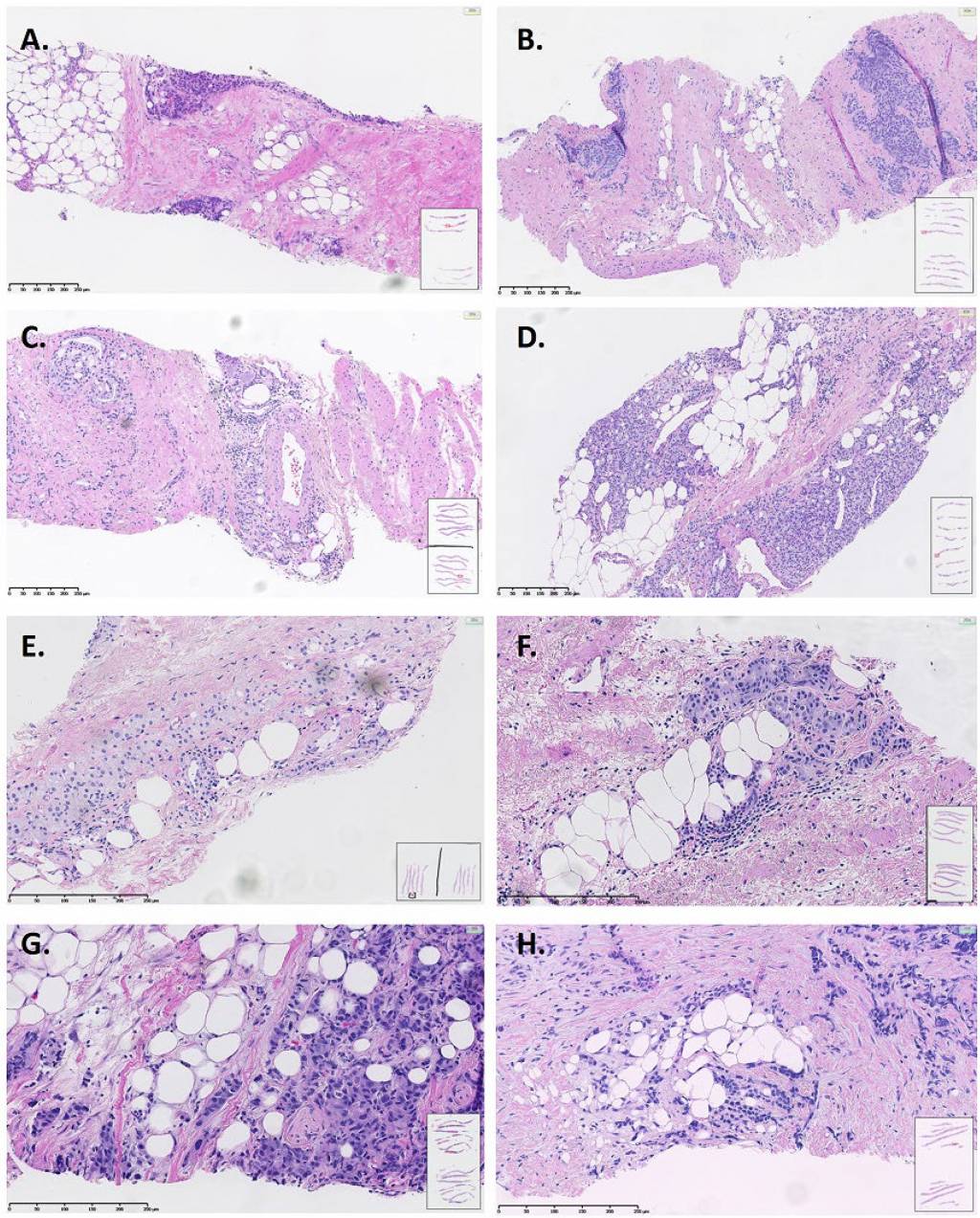 Extraprostatic extension (EPE+) in a needle biopsy may be more common than previously thought. Approximately one of six high grade prostate cancers harbor EPE+ in core biopsies. EPE+ is associated with highly adverse features of prostate cancer, making its reporting obligatory. More studies are needed to establish the predictive and prognostic value of EPE+ in needle biopsies
Extraprostatic extension (EPE+) in a needle biopsy may be more common than previously thought. Approximately one of six high grade prostate cancers harbor EPE+ in core biopsies. EPE+ is associated with highly adverse features of prostate cancer, making its reporting obligatory. More studies are needed to establish the predictive and prognostic value of EPE+ in needle biopsies
Tolonen TT, Riikonen J, Tammela TLJ, Koivusalo L, Haapasalo H, Kujala P, Kaipia A. Extraprostatic extension (pT3a) in prostate biopsy is an under-recognized feature indicating high risk disease.
Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Aug;35:80-84
